Surgical sutures which are also called the sutures are among the most preferred medical devices among other medical materials used for closing and sewing wounds (wound closure elements). Surgical sutures, whose discovery and usage date back 4000 years, have come a long way from the past to the present. With modern medicine, many different types of surgical sutures have been produced. Surgical sutures can be natural, synthetic, absorbable, unabsorbable, antibacterial, multifilament or monofilament options.
What Are The Types Of Surgical Sutures And Their Highlighted Features?
Knowledge Base
Let’s examine the surgical sutures and their highlighted features come in different varieties such as natural and synthetic surgical sutures.
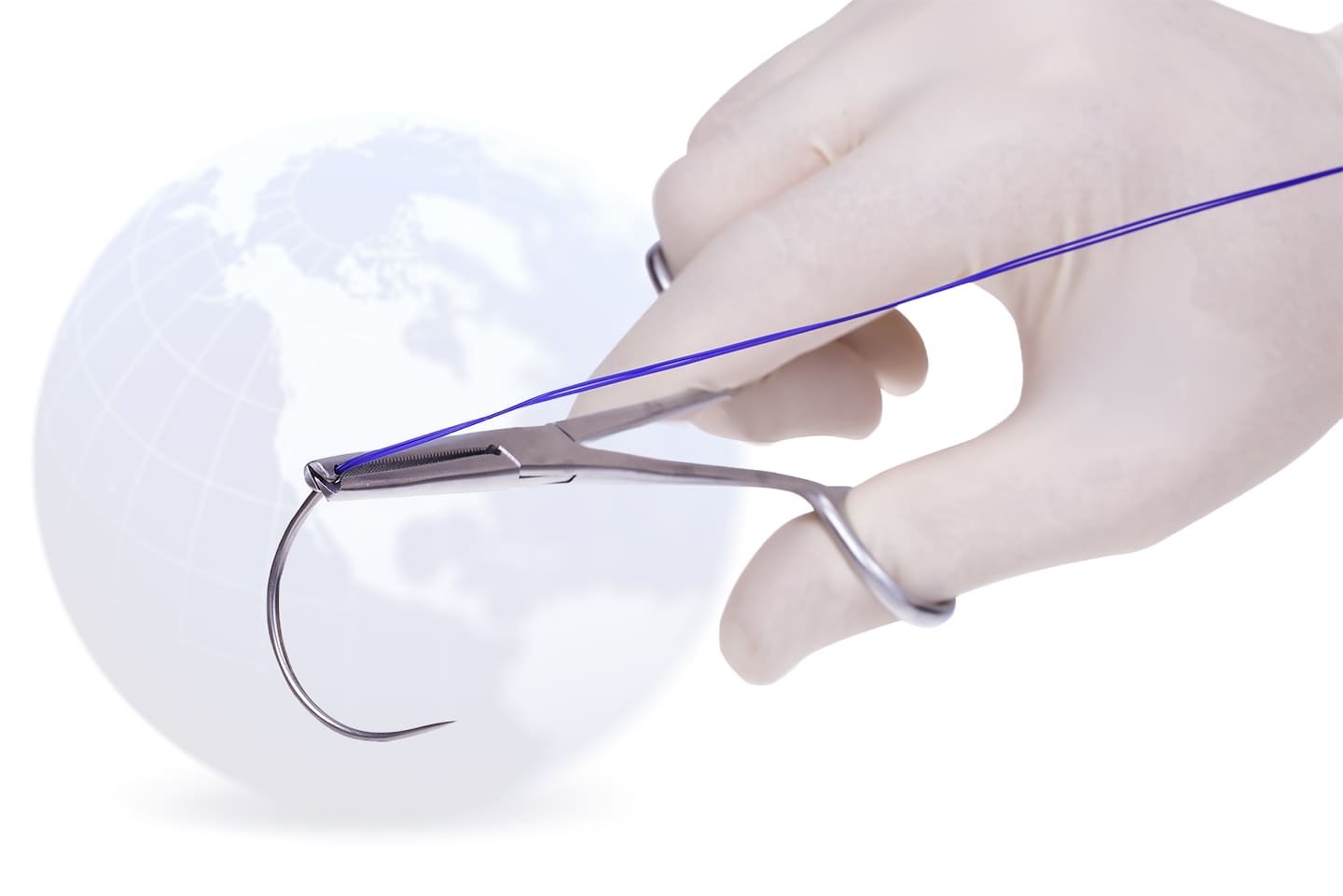
What Are Natural Surgical Sutures And What Are Their Types?
There are 2 different types when the surgical sutures are divided according to raw materials. These are natural surgical sutures and synthetic surgical sutures. The natural surgical sutures are divided into two categories. These are plant-based surgical sutures and animal product-based surgical sutures. The surgical sutures manufactured with these two raw materials from the nature can be categories as natural surgical sutures.
Plant-Based Surgical Sutures
Silk, which is the most widely used surgical suture today, is a sterile surgical suture consisting of non-absorbable organic polymer called fibroin. It is obtained from natural protein filaments derived from Bombyx Mori silkworm cocoon. (1, 2) Before the silk surgical suture is manufactured in the braided format, one of the 2 protein substances inside and the adhesive part are processed with wax and hum in the silk to be removed. This process gives a tighter knitting structure that significantly improves the quality of the braided and non-absorbable surgical suture produced from natural silk. After knitting, it is cooked and then coated with paraffin wax and silicone. (1, 2, 3)
Natural silk surgical sutures are the most preferred suture options around the world due to their softness, flexibility, thinness, ease of use and bonding properties. Due to its multi-filament (braided) structure, it has high capillary properties and requires very few nodes in terms of node safety. Surgical natural silk sutures are used for soft tissue closure or binding, including cardiovascular, ophthalmic and neurosurgery applications. (1.2)
Animal-Based Surgical Sutures
This is an absorbable natural products called catgut which was named from a violin called “Kit” by the ancient Egyptians Arabs and it is referred as a surgical gut. During the production of this surgical suture which includes the submucous porous tissue of the sheep’s intestine or the serosa membrane of the cows, the parts of the connective tissue, which are cleaned with special care and whose oil is taken, are reconstituted, twisted and dried until the desired thickness is reached. (1, 4, 5)
In addition to the normal use of catgut sutures, it is treated with the necessary chrome salt solutions for the purpose of extending the absorption time. For this reason, the catgut surgical sutures are divided into normal catgut and chromium catgut in the medical field. (1,4,5)
What Are the Synthetic Surgical Sutures and Their Types?
Synthetic raw materials, which do not occur naturally and are created by human efforts, are used in the production of many medical devices in today’s health field. Synthetic raw materials, which provide many advantages especially in the production of surgical suture, have greatly contributed to the development of surgical sutures.
The types of synthetic surgical sutures used today are divided into different categories which are monofilament (straight) and multifilament (braided) as well as absorbable and non-absorbable. Synthetic surgical suture types with different chemical structures provide ease of use in many surgical branches, as well as low reaction and high strength in the tissue. (18,19)
Polyglycolic Acid (PGA) Surgical Sutures
This type which is a homo-polymer of glycolic acid, is the first synthetic, absorbable surgical suture and was first introduced in 1970. This type of suture with synthetic structure has delayed absorption and reduced tissue reaction compared to catgut sutures, as well as good tensile and better knot strength. Similar to chromic catgut, it shows absorption and polyester (PET)-like strength and knot safety.
Made from polyglycolic acid, these synthetic and absorbable surgical sutures have a multifilament structure and can also be coated with polycaprolactone, a synthetic coating to ensure smooth tissue transition and seamless knot bonding. (1,6,7)
Poly Glycolide Lactide Acid (PGLA) Surgical Sutures
Poly glycolide lactide acid (PGLA) which is another type of absorbable synthetic surgical suture is flexible, absorbable and poly [%90 glycolide + 10% lactide] (glycolic and lactide acid derivative), which can be absorbed when used in living organisms and does not cause excessive irritation in tissue. Striped variations of surgical sutures whose chemical structure is Poli Glycolide Lactide acid (PGLA) use Poli (Glycolide Lactide) (30/70) and calcium stearate as special coating agent. (20)
Poly Glycolide Caprolactone (PGCL) Surgical Sutures
Polyglycolidcocaprolacton PGCL, a synthetic type of surgical suture synthesized from caprolactone and found in a monofilament structure, provides high node safety in closing superficial wounds such as sterile surgical filament dental operations and does not cause excessive tissue irritation throughout absorption. (9)
Produced in two different colors, colorless and purple (violet), EO (ethylene oxide) sterilized and chemically manufactured from 75% Glycolide and 25% co-caprolactone, synthetic and absorbable PGCL surgical sutures provide 45%-70% tissue support in the first week and are completely absorbed by the body within 90-120 days. (8, 9)
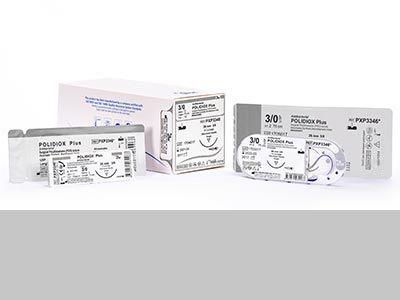
Polydioxanone (PDO) Surgical Sutures
Manufactured from polydioxanone poly (p-dioxanone) polyesters, Polydioxanone (PDO) has a monofilament structure and is a type of synthetic sterile surgical suture. Polydioxanone polymer has a nonantigenic and nonpyrogenic structure. The empirical molecular formula of the polymer is (C₄H₆O₃)x and polydioxanone surgical sutures can cause light tissue reaction during absorption by the body. (10)
To ensure visibility in surgical operations, Polydioxanone (PDO) absorbable surgical sutures are purple (violet) colored and sterilized with EO (ethylene oxide) and used including ophthalmic applications and pediatric cardiovascular tissue where growth is expected to occur. Synthetic and absorbable PDO surgical sutures with chemical structure of 100% Polydioxanone provides 70% tissue support in 2 weeks and is fully absorbed by the body within 180-240 days. (10, 11)
Polypropylene (PP) Surgical Sutures
Manufactured from the stereoisomer of the isotactic crystal of polypropylene, the chemical structure of polypropylene (PP), a type of synthetic surgical suture with monofilament structure that is usually produced in blue or black to enhance its appearance during surgical intervention. Further, it is synthetic linear polyolefin, consisting of the stereoisomer of the isotactic crystal of polypropylene. (12)
Polypropylene sutures that used in general soft tissue closure and binding, including cardiovascular, ophthalmic and neurosurgery applications, are often used in general surgery, soft tissue approximation and ligation, fascia stitching, patch detection and skin closure (both individually and subcuticular). It is used in almost all surgical areas, including cardiovascular, orthopedic, eye, microsurgery and neurological surgery. It is the type of surgical suture used in the vascular suturing the anastomoses due to its slippery and elastic structure. (13, 14)
Polyamide (PA) Surgical Sutures
Non-absorbable and sterile Polyamide (PA) surgical sutures which are the first synthetic surgical strand are manufactured in two different type as monofilament and multifilament consisting of long-chain chains of aliphatic polymer chemically known as nylon 6 or nylon 6.6 come in black or blue color to increase visibility in the tissue. (1, 15)
Known for its high tensile strength, excellent elastic properties and minimal tissue reaction, polyamide (PA) non-absorbable surgical sutures are used in general soft tissue closure and binding, including cardiovascular, ophthalmic and neurosurgery applications. (1, 15)
Polyvinyl Difluoride (PVDF) Surgical Sutures
Known as polyvinyl fluoride or polyvinyl difluoride (PVDF), it is a non-reactive thermoplastic produced by polymerization of vinylene difluoride. Sterile, non-absorbable PVDF surgical sutures consisting of polyvinyl difluoride polymer has monofilament structure and dyed blue and black to increase visibility. (16, 17)
In addition to its strong and flexible structure, the surgical suture sterilized with EO (ethylene oxide) is resistant to infection. It is successfully used in infected or contaminated wounds to minimize or eliminate subsequent sinus formation and excretion of the suture. (16, 17)
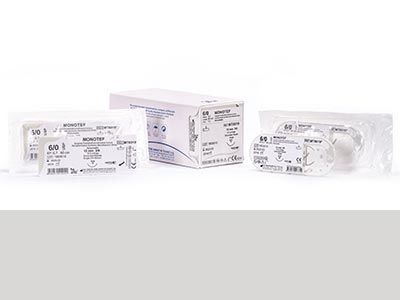
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Surgical Sutures
Non-absorbable, monofilament and synthetic surgical sutures made of 100% Polytetrafluoroethylene are produced from high density 100% polytetrafluoroethylene by pulling to maintain integrity and tensile strength, as well as to produce a structure with a minimum pore size and volume.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) surgical sutures are often preferred in cardiovascular surgery, dental treatment and eye surgery, show excellent biocompatibility, provide high knot strength and have an extremely low friction coefficient. (21, 22)
Polyester (PET) Surgical Sutures
Polyester (PET) surgical sutures made of long-chain linear polyester, with high molecular weight and composed of Polysyl Poly (ethylene terephthalate) are multifilament and synthetic surgical sutures. The surgical suture with Polyester (PET) comes with either coated or uncoated silicone elastomer form. The coating material, which has high adhesive strength in the tissue, is not reactive and is sterilized with EO (Ethylene oxide).
The non-absorbable coating provides permanent tissue support and acts as a lubricant. This property enables the synthetic structure to easily pass from the tissue as well as ease-of-use. Polyester (PET) synthetic non-absorbable surgical sutures are often used to seal and bind general soft tissues, including cardiovascular, ophthalmic and neurosurgery applications. (23)
Bibliography
(1) 1. GEMCİ R., ULCAY Y. (2004). Ameliyat İplikleri Tipleri Özellikleri ve Krome Katgüt İle Normal Katgüt Arasındaki Mukavemet Farkları. Uludağ Üniversitesi Mühendislik Mimarlık Fakültesi Dergisi, Cilt 9, Sayı 2, 2004
(2) İpek – Silk – Boz Tıbbi Malzemeler. (2022, Ağustos 03). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilmeyen-suturler/ipek-silk
(3) İpek Dental Sütür Emilmeyen Ameliyat İpliği. (2022, Ağustos 03). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/cerrahi-branslara-ozel-suturler/agiz-dis-ve-cene-cerrahisi-suturleri/ipek-dental-sutur-emilmeyen-ameliyat-ipligi
(4) Chromic Catgut – Emilebilir Cerrahi Ameliyat İpliği | Sütür. (2022, Ağustos 03). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilebilir-suturler/chromic-catgut
(5) Plain Catgut – Emilebilir Sütür, Cerrahi Ameliyat İpliği. (2022, Ağustos 03). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilebilir-suturler/plain-catgut
(6) Fastsorb (PGA) – Hızlı Emilebilir Sütür, Cerrahi Ameliyat İpliği. (2022, Ağustos 19). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilebilir-suturler/fastsorb
(7) Glikosorb (PGA) – Emilebilir Sütür, Cerrahi Ameliyat İpliği. (2022, Ağustos 19). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilebilir-suturler/glikosorb
(8) Monokaprol (PGCL) – Emilebilir Sütür, Cerrahi Ameliyat İpliği. (2022, Aralık 06). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilebilir-suturler/monokaprol
(9) Poliglikolidkokaprolakton PGCL Dental Sütür – Monokaprol. (2022, Aralık 06). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/cerrahi-branslara-ozel-suturler/agiz-dis-ve-cene-cerrahisi-suturleri/poliglikolidkokaprolakton-pgcl-dental-sutur-monokaprol
(10) Polidiox (PDO) – Emilebilir Sütür, Cerrahi Ameliyat İpliği. (2022, Aralık 06). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilebilir-suturler/polidiox
(11) Polidiox – Emilebilir PDO Polidiaksanon Veteriner Sütürü. (2022,Aralık 06). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/cerrahi-branslara-ozel-suturler/veteriner-cerrahisi-suturleri/polidiox-emilebilir-cerrahi-veteriner-suturu
(12) Monoprolen – Boz Tıbbi Malzemeler. (2022, Aralık 06). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilmeyen-suturler/monoprolen
(13) Polipropilen Sütür | turkcerrahi.com. (2022, Kasım 14). Erişim adresi: https://www.turkcerrahi.com/tip-sozlugu/polipropilen
(14) Anastomoz – TIPlopedi. (2022, Aralık 06). Erişim adresi: https://tiplopedi.com/Anastomoz
(15) Monamid – Boz Tıbbi Malzemeler. (2022, Aralık 07). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilmeyen-suturler/monamid
Bibliography (Part 2)
(16) Monoflorid – Boz Tıbbi Malzemeler. (2022, Aralık 07). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilmeyen-suturler/monoflorid
(17) PVDF – Polivinil Florür – NSB Polymers GmbH Germany. (2021, Mart 14). Erişim adresi: https://nsb-polymers.de/tr/pvdf-polivinil-florur
(18) CNN TÜRK. (2021). Sentetik Ne Demek? Tdk’ya Göre Sentetik Kelime Anlamı Nedir, Nasıl Kullanılır? CNN TÜRK. Erişim adresi: https://www.cnnturk.com/kultur-sanat/sentetik-ne-demek-tdkya-gore-sentetik-kelime-anlami-nedir-nasil-kullanilir
(19) Çetinkaya, Ömer Arda. “Cerrahi Sütür Materyalleri ve Uygulaması” (erişim 24.01.2023)
(20) Glikolak (PGLA) – Emilebilir Sütür, Cerrahi Ameliyat İpliği. (2023, Ocak 21). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilebilir-suturler/glikolak
(21) Monotef Emilmeyen Sütür, Cerrahi Ameliyat İpliği – Boz Tıbbi Malzemeler. (2023, Şubat 21). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilmeyen-suturler/monotef
(22) Politetrafloroetilen PTFE Dental Dikiş İpliği – Monotef. (2023, Ocak 21). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/cerrahi-branslara-ozel-suturler/agiz-dis-ve-cene-cerrahisi-suturleri/politetrafloroetilen-ptfe-dental-dikis-ipligi-monotef
(23) Polisil Emilmeyen Sütür, Cerrahi Ameliyat İpliği – Boz Tıbbi Malzemeler. (2023, Ocak 21). Erişim adresi: https://www.boztibbi.com/urunler/suturler/emilmeyen-suturler/polisil